Polynomial Division Over Finite Field
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. F x3 1.
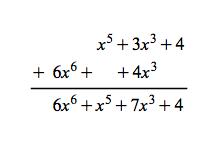
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic
There are only two such polynomials.
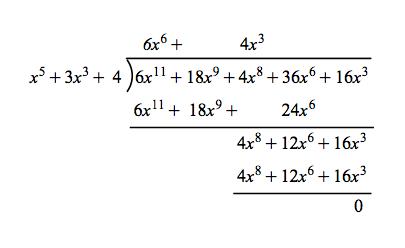
Polynomial division over finite field. We carry out division with remainder dividing f by the polynomial x - alpha. Fx x - alphaqx beta beta in mathbb F_pn Inserting x alpha in the above equation proves beta 0 and f x - alphaq contradicting irreducibility. Consider again the polynomials defined over GF7.
If not how to manually typeset long division in general. For polynomials a x b x and g x which are over the same field we say a x is congruent to b x modulo g x written a x b x mod g x if m x divides a x - b x. In particular these results are studied when one studies normal forms for finitely-generated modules over a PID eg.
However the vertical spacing between each line and exponents of the equation below it is quite small how to increase it. Represent the polynomials as row vectors character vectors and strings. In particular Theorem 12 implies that a DFT of length over a finite field can be computed in time on a Turing machine.
Hparent Fraction Field of. Represent the polynomials using row vectors and divide them in GF 3. Cite PARI in your work as well.
The polynomial P x4 1 is irreducible over Q but not over any finite field. On every other finite field at least one of 1 2 and 2 is a square because the product of two non-squares is a square and so we have If. X 3 x 2 1 and x 3 x 1.
H x3 1 x2 - 17 sage. A polynomial m x is called irreducible if and only if m x cannot be expressed as a product of two poly- nomials both of degree lower than that of m x. The polynomial r x is called the remainder of f x modulo g x.
Then there exists unique q r in Fx such that fx gxqx rx with the property that either rx 0 or degr degg. G x2 - 17 sage. For example all polynomials are over GF 3.
The elements of F x are called polynomials over F. Dividing two polynomials constructs an element of the fraction field which Sage creates automatically. I attempted the following solution.
On any field extension of F2 P x 1 4. Addition is equivalent to taking the XOR of. Polynomial ring rm Fx for rm F a field as above.
Let F cdot be a field and let f g in Fx with gx neq 0. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Dividing polynomials defined over a finite field is a little bit more frustrating than performing other arithmetic operations on such polynomials.
Lets say we want to divide 5x2 4x 6 by 2x 1. There are many irreducible polynomials sometimes called reducing polynomials that can be used to generate a finite field but they do not all give rise to the same representation of the field. Self-reciprocal polynomials over finite fields are used to generate reversible codes with a read-backward property J.
Q_rvr_rv gfdeconv bap q_rv 14 1 0 0 1. X QQx0 sage. The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of variable in it.
When one studies linear systems of equations with coefficients in the non-field. Divide by in the Galois field GF 3 three times. Is there a package like polynom for typesetting polynomial long division but over a finite field such as GF2.
A monic irreducible polynomial of degree n having coefficients in the finite field GF q where q p t for some prime p and positive integer t is called a primitive polynomial if all of its. For example to construct the finite field GF2 3 we need to choose an irre- ducible polynomial of degree 3. A polynomial f x of positive degree is said to be reducible over F if there e xist two polynomials g x and h x over F such that 1 deg g x deg h x deg f.
Now your mental gymnastics must include both additive inverses and multiplicative inverses. Nussbaumer polynomial transforms 42 43 constitute yet another essential tool for our new results. Theorem 1 The Division Algorithm for Polynomials over a Field.
Extended polynomial GCD in finite field The calculator computes extended greatest common divisor for two polynomials in finite field. A 1 1. In a similar way as in SchönhageStrassens second algorithm from 49 the idea is to use DFTs over a ring with.
B 0 1 0 1 1.

Polynomial Long Division Over Gf P Tex Latex Stack Exchange

Addition And Multiplication In A Galois Field Mathematics Stack Exchange
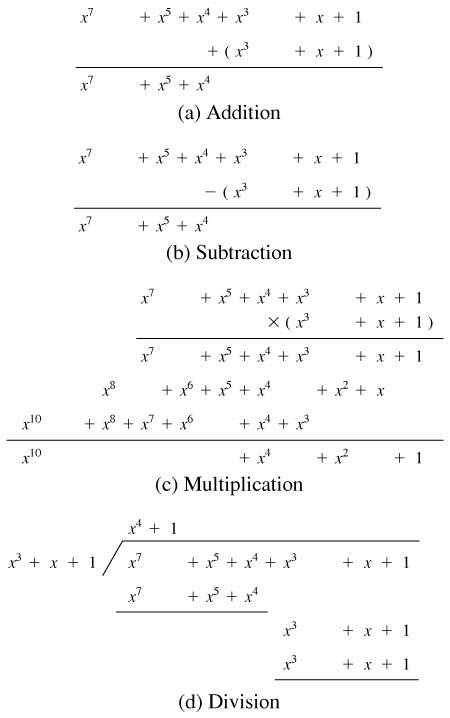
Section 4 5 Polynomial Arithmetic Cryptography And Network Security 4th Edition

Division In Finite Fields Mathematics Stack Exchange

Performing Division And Multiplication Over Gf P Mathematics Stack Exchange

Polynomial Long Division Over Gf P Tex Latex Stack Exchange
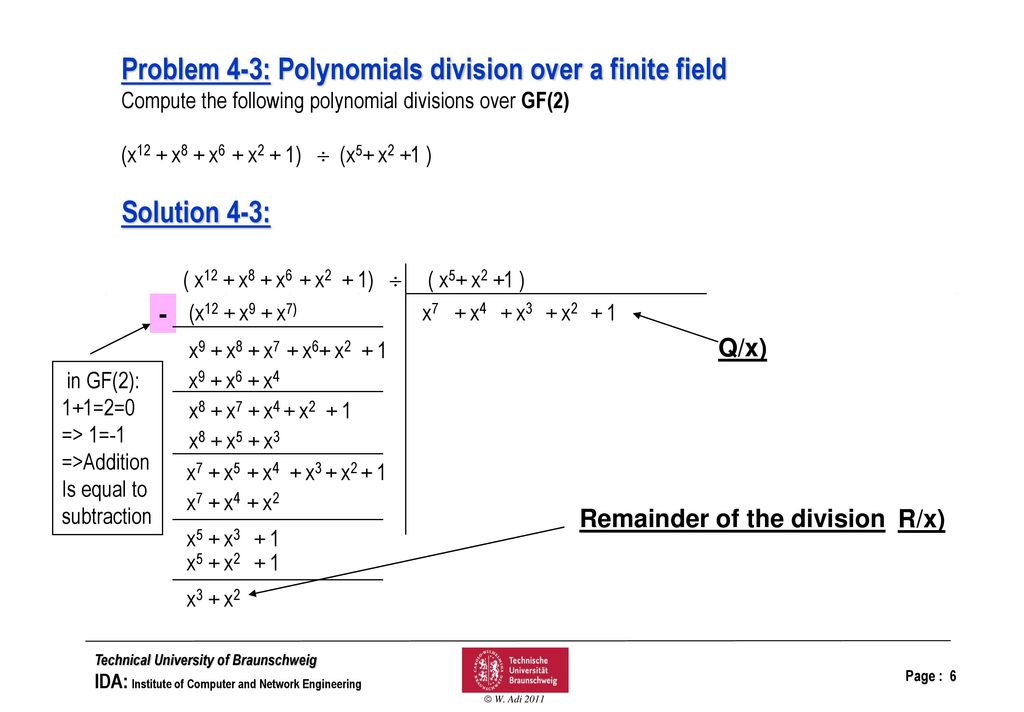
Mathematical Background Extension Fields Ppt Download

Addition And Multiplication In F 4 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Finite Fields Of The Form Gf 2n
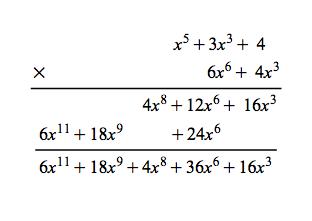
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic
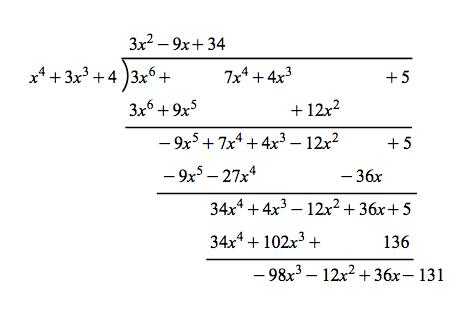
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic
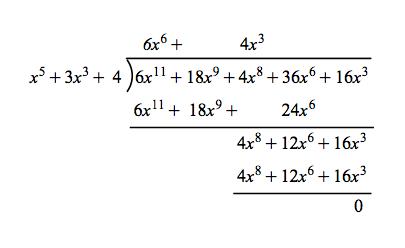
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic

Finding The Greatest Common Divisor Of Polynomials Over A Finite Field Youtube
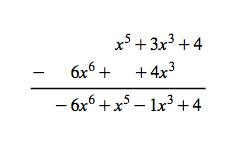
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic
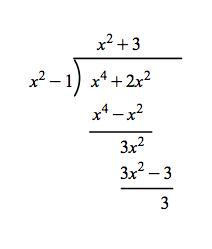
Galois Theorem And Polynomial Arithmetic

Finding The Gcd Of Two Polynomials Over A Finite Field Youtube